Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has come a long way since the internet’s early days. What began as a few simple tricks to get websites noticed has now grown into a sophisticated digital marketing discipline powered by artificial intelligence. Understanding how SEO evolved helps beginners see why it’s such an important part of building an online presence today.
Who Invented SEO?
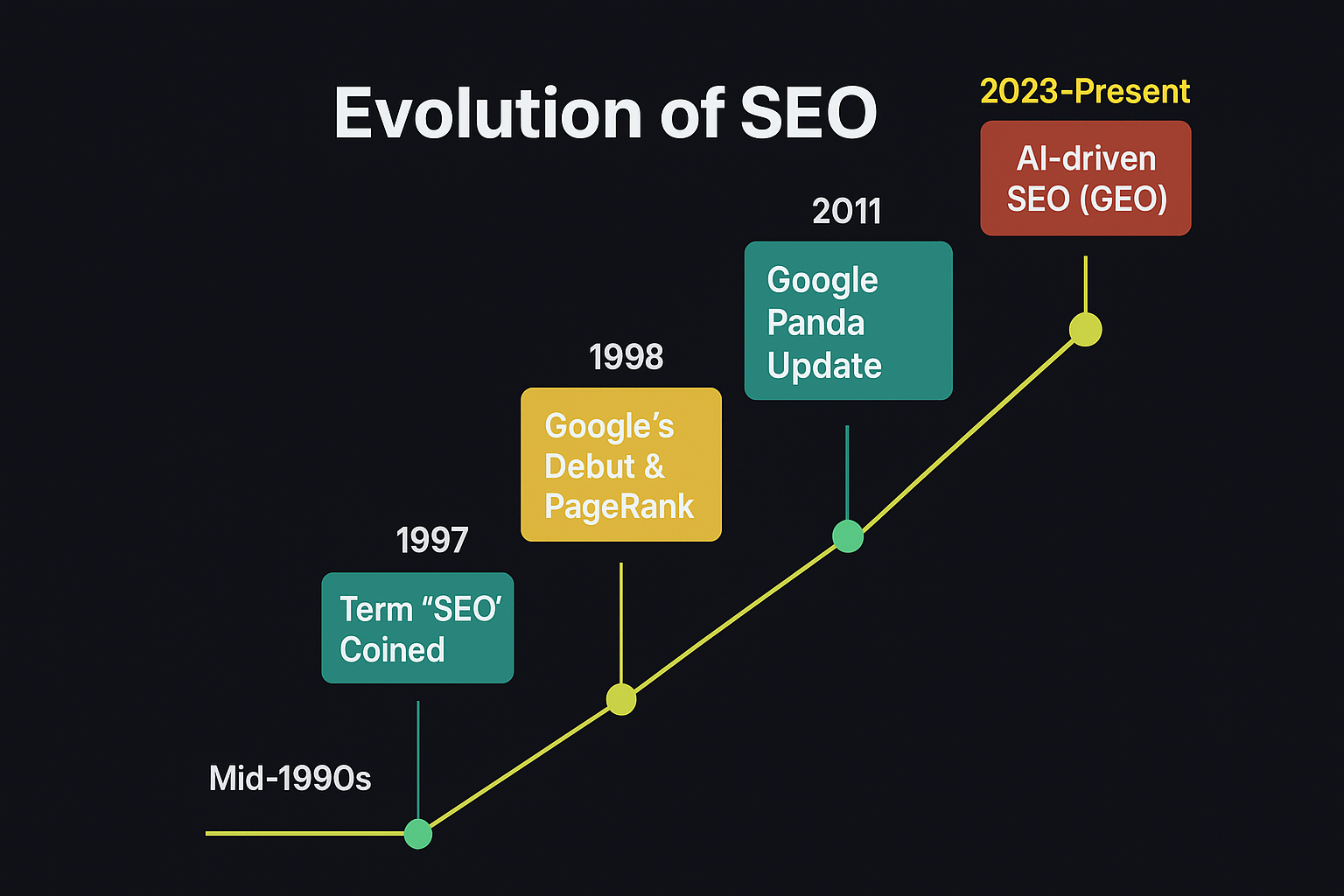
SEO doesn’t have a single “inventor,” but the concept emerged as website owners competed for visibility on early search engines like Yahoo and AltaVista. In 1997, Bruce Clay popularized the term Search Engine Optimization and helped shape the industry.
With Google’s launch in 1998, SEO evolved from simple page submissions to strategies focused on links, relevance, and authority. What began as a technical practice has grown into a multi-billion-dollar digital marketing industry, now powered by AI tools that analyze search patterns and deliver results tailored to user intent.
History of SEO & When Did It Start?
The first steps of SEO appeared in the mid-1990s, when early search engines indexed websites using basic signals like meta tags, titles, and keywords. Back then, ranking was easy to manipulate with keyword stuffing and mass directory submissions.
Things changed dramatically in 1998 when Google launched its PageRank algorithm, which rewarded websites with quality links rather than just keyword use. This marked the shift from simple tricks to strategies based on authority, relevance, and trustworthiness.
As Google grew, major updates like Panda, Penguin, and BERT cracked down on spammy tactics and pushed SEO toward high-quality content and user-focused search. Today, in 2025, SEO has entered the age of AI-driven search and Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) — where voice search, semantic indexing, and machine learning favour well-structured, relevant, and real-time information.
SEO Evolution Timeline
2000–2005 – SEO Becomes an Industry
The early 2000s marked the moment SEO stopped being just a technical trick and started becoming a full-fledged digital marketing industry. As Google gained dominance over search, businesses realised that ranking higher wasn’t optional anymore — it was essential for growth.
In 2000, Google launched AdWords, its advertising platform, proving that search visibility could directly drive revenue. At the same time, its PageRank system continued to prioritise high-quality backlinks, forcing website owners to think beyond keyword stuffing and focus on authority building.
Major Google updates shaped this period:
• 2003 – Florida Update: This was the first major algorithm update, wiping out sites using manipulative tactics like keyword stuffing and link farms. It signalled the end of “black-hat SEO” as a shortcut to the top.
• 2004 – Brandy Update: Introduced concepts like link relevance, latent semantic indexing (LSI) for understanding context, and more importance on “topic-focused” websites.
2006–2010 – Rise of Local SEO and Google Analytics
Between 2006 and 2010, SEO entered a new phase as search engines became smarter and users demanded more relevant, location-based results. Google shifted its focus from simply ranking websites globally to providing personalised and localised search experiences.
Key developments during this era:
• 2006 – Launch of Google Analytics: Google acquired Urchin and turned it into Google Analytics, giving website owners powerful insights into visitor behaviour, traffic sources, and conversions. For the first time, marketers could track SEO performance with precision and make data-driven decisions.
• 2007 – Universal Search: Google began blending different types of results — websites, images, news, maps, and videos — onto the same results page. This changed SEO forever, requiring optimisation across multiple content formats rather than just text.
• 2008 – Google Suggest: Autocomplete in search results gave businesses clues into real user search intent, influencing keyword strategies.
• 2009 – Vince Update: Google started prioritising trusted brands in search results, rewarding authority and credibility. This update marked the beginning of SEO favouring established entities over thin affiliate sites.
• 2010 – Google Places and Local SEO: Google launched Google Places, integrating maps and business listings directly into search. This gave rise to Local SEO, where businesses optimised for nearby customers using reviews, NAP (Name-Address-Phone) consistency, and geo-targeted keywords.
Tools and strategies advanced rapidly. SEOs now used Google Webmaster Tools (now Search Console), keyword research tools like Wordtracker, and early versions of SEMrush and Moz to analyse backlinks and rankings.
By 2010, SEO had evolved from being purely technical into a blend of brand building, local visibility, and user experience optimisation. Search was no longer one-size-fits-all — it was becoming personalised, measurable, and competitive, laying the groundwork for mobile and AI-driven search in the next decade.
2011–2015 – Algorithm Overhauls: Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird
From 2011 to 2015, Google radically reshaped SEO by launching major algorithm updates designed to improve search quality and eliminate manipulation. These years marked the end of “quick-win” tactics and the rise of content-focused, user-first SEO.
Key developments during this era:
• 2011 – Panda Update: Google cracked down on thin, low-quality content and keyword stuffing. Sites with duplicate or shallow content saw dramatic ranking drops, forcing SEOs to focus on originality and value.
• 2012 – Penguin Update: Penguin targeted link spam, penalising websites using paid links, link farms, or unnatural backlink profiles. Ethical link-building strategies became critical.
• 2013 – Hummingbird Algorithm: Google introduced Hummingbird, which emphasised semantic search and understanding user intent rather than matching exact keywords. This was an early move toward conversational search and laid the groundwork for voice search.
• 2014 – HTTPS as a Ranking Signal: Security became a priority as Google encouraged websites to adopt SSL certificates for better rankings.
• 2015 – Mobile-Friendly Update (“Mobilegeddon”): With mobile searches surpassing desktop, Google began rewarding mobile-optimised websites, pushing responsive design into the mainstream.
Tools and SEO practices matured quickly. Marketers leaned heavily on Google Analytics, Search Console, Moz, Ahrefs, and SEMrush to track performance, audit sites, and fix penalties. SEO agencies shifted from bulk link-building to content marketing, technical SEO, and digital PR.
By 2015, SEO was no longer about tricking search engines — it was about earning trust through relevant content, strong brands, and excellent user experiences. These updates forced businesses to adapt or disappear, solidifying SEO as a professional discipline rather than an experimental tactic.
2016–2020 – Rise of AI, RankBrain, and Mobile-First Indexing
Between 2016 and 2020, Google integrated artificial intelligence into its ranking systems, signalling the start of SEO’s AI-driven era. Search became smarter, prioritising context, intent, and user experience over traditional keyword signals.
Key developments during this era:
• 2016 – RankBrain Fully Integrated: Google’s machine-learning system, RankBrain, became a core part of the algorithm. It helped Google interpret ambiguous or long-tail queries by analysing patterns and user behaviour, rewarding websites with well-structured, context-rich content.
• 2017 – Mobile-First Indexing Announced: With mobile traffic surpassing desktop, Google shifted to indexing and ranking websites based primarily on their mobile versions. Responsive, fast-loading websites became essential.
• 2018 – Medic Update: This update heavily affected health, finance, and other “Your Money, Your Life” (YMYL) sites, emphasising E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) as key ranking factors.
• 2019 – BERT Algorithm: Google introduced BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), enabling better understanding of natural language and context within searches. This made content quality, semantic relevance, and topic depth more important than ever.
• 2020 – Passage Indexing and Core Web Vitals: Google began ranking specific passages from pages, not just entire pages. It also introduced Core Web Vitals as performance metrics for user experience, focusing on speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
SEO tools evolved too. Platforms like SEMrush, Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, and SurferSEO added AI-driven audits, content recommendations, and advanced keyword clustering. Marketers started optimising for voice search, structured data (schema), and featured snippets to capture emerging search formats.
By 2020, SEO was no longer just about ranking pages — it was about delivering fast, mobile-friendly, intent-focused content that matched how real people search, with AI guiding both Google’s results and SEO strategies.
2021–2025 – AI Search, MUM, and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
From 2021 to 2025, SEO entered its most transformative era yet, driven by artificial intelligence, advanced machine learning, and Google’s Multitask Unified Model (MUM). Search evolved beyond simple results — it became predictive, conversational, and generative.
Key developments during this era:
• 2021 – Google MUM Announced: MUM, 1,000 times more powerful than BERT, could understand information across text, images, and video, providing deeper context and multi-step query understanding.
• 2022 – Helpful Content Update: Google began prioritising people-first content over SEO-first articles, rewarding websites offering genuine value and penalising mass-produced, low-quality pages.
• 2023 – AI Search & Generative Results: Search engines, led by Google and Bing, integrated AI-driven overviews and conversational search powered by large language models. SEOs adapted to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) to ensure visibility within AI summaries.
• 2024 – EEAT Strengthened: Google added “Experience” to Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, rewarding content created by real experts with proven firsthand knowledge.
• 2025 – Real-Time, Predictive SEO: Search engines now personalise results using AI-driven context, user behaviour, and intent prediction, while websites leverage AI tools to create dynamic, optimised, and semantically rich content.
SEO strategies fully embraced AI. Tools like ChatGPT, Jasper, SurferSEO, and Clearscope powered scalable content optimisation, while Google Search Console integrated predictive analytics. Voice search, visual search, and zero-click results became standard, requiring businesses to optimise beyond blue links.
By 2025, SEO is less about chasing algorithms and more about understanding users, delivering real value, and aligning with AI-powered search experiences. GEO represents the future — where content must be structured, authoritative, and contextually relevant to appear in both traditional rankings and AI-generated answers.
Conclusion: Mastering SEO in 2025
SEO has evolved from simple keyword tricks in the early 2000s to today’s AI-powered, user-first strategies. In 2025, success comes from understanding how people search, not just how algorithms rank. The focus is no longer on chasing loopholes but on building credibility, authority, and value across every touchpoint.
Actionable SEO Tips for 2025:
• Optimise for AI Overviews (GEO): Structure content with clear headings, FAQs, and schema markup so it can be pulled into generative AI results.
• Prioritise EEAT: Showcase real expertise, author profiles, case studies, and firsthand experiences to build authority and trust.
• Create Multi-Format Content: Blend text, images, video, and even audio to meet MUM’s multimodal search capabilities.
• Focus on Core Web Vitals: Ensure your site is lightning fast, mobile-first, and visually stable to rank in both traditional and AI-driven results.
• Write for People, Not Just Search Engines: Helpful, original, and user-focused content wins over SEO-first copy.
The future of SEO belongs to businesses that combine human value with AI adaptability. If you invest in trust, relevance, and real user experience, your visibility in 2025 and beyond will take care of itself.